How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a question many aspiring pilots ask. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of drone operation, from pre-flight checks and safety procedures to mastering flight controls and capturing stunning aerial photography. We’ll cover everything you need to know to confidently take to the skies, ensuring a smooth and enjoyable experience.
Understanding the basics of drone control, including throttle, yaw, pitch, and roll, is crucial. We’ll explore various flight modes and control methods, helping you choose the approach best suited to your skill level and the specific drone model you’re using. Beyond the technical aspects, we’ll delve into essential flight planning, considering weather conditions, airspace regulations, and battery life to guarantee safe and responsible operation.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
A thorough pre-flight checklist is crucial for safe and responsible drone operation. It minimizes risks and ensures your flight proceeds smoothly. This section details the essential steps and safety regulations to follow before each flight.
Understanding drone operation involves mastering several key skills, from pre-flight checks to navigating airspace regulations. Successfully piloting a drone requires practice and knowledge, and a great resource for learning is available at how to operate a drone , which offers comprehensive guides and tutorials. Ultimately, safe and effective drone operation hinges on consistent practice and a thorough understanding of the technology and its limitations.
Pre-Flight Inspection
Before each flight, conduct a comprehensive inspection. This involves checking the drone’s battery level, propeller condition, and GPS signal strength. Ensure all components are securely attached and functioning correctly.
- Check the drone’s battery level and ensure it is adequately charged for the planned flight duration.
- Inspect the propellers for any damage, cracks, or imbalances. Replace any damaged propellers before flight.
- Verify a strong GPS signal is acquired. A weak signal can lead to inaccurate positioning and control issues.
- Visually inspect the drone’s body and arms for any damage or loose parts.
- Confirm the remote controller is properly paired with the drone and has sufficient battery power.
Safety Regulations and Best Practices
Adhering to safety regulations and best practices is paramount. This includes understanding airspace restrictions and having a plan for emergencies.
- Check for any temporary flight restrictions (TFRs) in your planned flight area using a flight planning app or website.
- Maintain visual line of sight with your drone at all times. Do not fly beyond your visual range.
- Avoid flying near airports, heliports, or other restricted airspace.
- Never fly your drone over people or crowds.
- Be aware of the weather conditions and avoid flying in strong winds, rain, or snow.
- Have a backup plan in case of unexpected issues, such as battery failure or GPS signal loss.
Pre-Flight Checklist Table
Use this checklist before every flight to ensure a safe and successful operation.
| Item | Check | Action | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Battery Level | Charge if necessary | Ensure sufficient charge for flight time | |
| Propeller Inspection | Replace damaged propellers | Check for cracks or damage | |
| GPS Signal | Wait for a strong signal | Ensure accurate positioning | |
| Remote Controller Connection | Pair if necessary | Verify controller battery | |
| Airspace Check | Check for restrictions | Use a flight planning app | |
| Weather Conditions | Postpone flight if necessary | Avoid strong winds, rain, or snow |
Understanding Drone Controls and Navigation
Understanding your drone’s controls is fundamental to safe and effective operation. This section explains the basic controls, flight modes, and control methods.
Basic Drone Controls
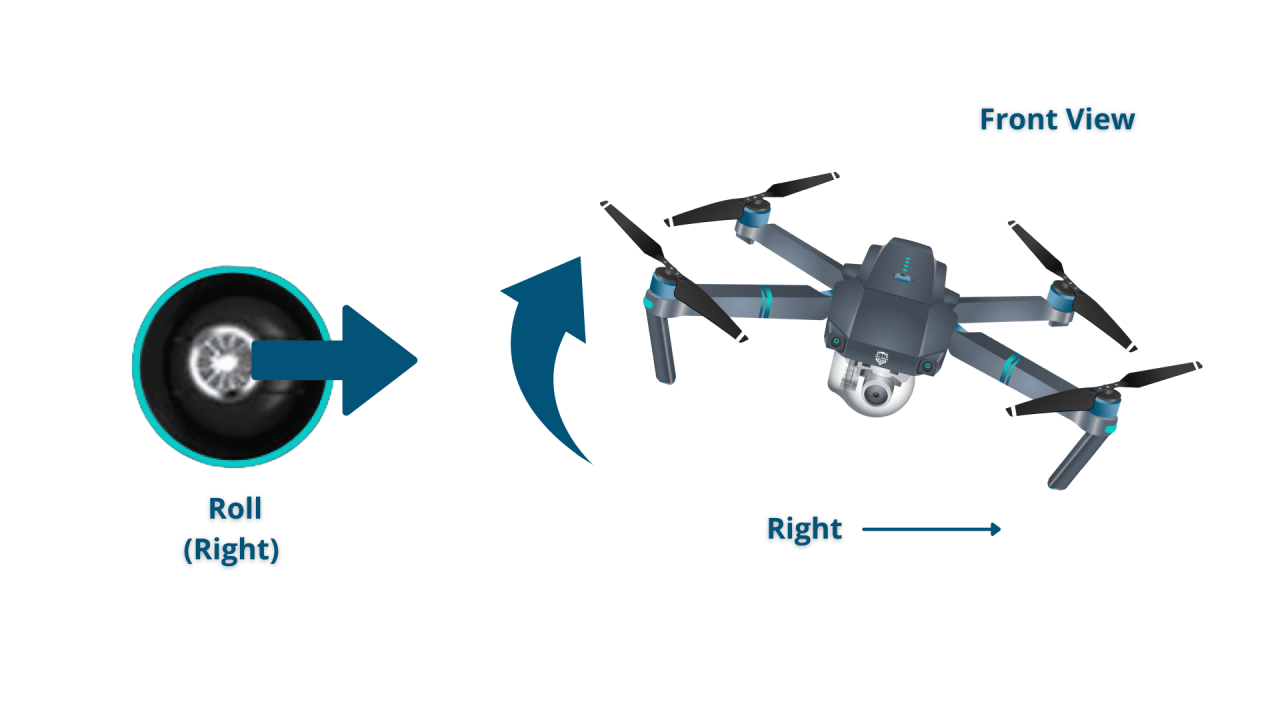
Most drones use a set of four primary controls: throttle, yaw, pitch, and roll. Mastering these controls is crucial for stable flight.
- Throttle: Controls the altitude of the drone (up and down).
- Yaw: Controls the drone’s rotation around its vertical axis (left and right).
- Pitch: Controls the drone’s movement forward and backward.
- Roll: Controls the drone’s movement left and right.
Flight Modes
Many drones offer different flight modes to suit various skill levels and flight situations. Beginner mode often limits speed and responsiveness, while sport mode allows for more agile maneuvers.
- Beginner Mode: Limits speed and responsiveness, ideal for learning.
- Sport Mode: Enables faster speeds and more aggressive maneuvers for experienced pilots.
- GPS Mode: Uses GPS for precise positioning and stability.
- Attitude Mode: Maintains the drone’s orientation relative to the pilot, regardless of GPS signal.
Drone Control Methods
Drones can be controlled using either a dedicated joystick controller or a mobile app. Each method has its advantages and disadvantages.
- Joystick Controller: Offers precise control and tactile feedback, ideal for complex maneuvers.
- Mobile App: Provides a user-friendly interface and access to additional features, but may lack the precision of a joystick.
Taking Off, Hovering, and Landing, How to operate a drone
Here’s a step-by-step guide for safe takeoff, hovering, and landing procedures.
- Ensure the drone is calibrated and has a strong GPS signal.
- Gently increase the throttle to lift off the ground.
- Use the yaw, pitch, and roll controls to maintain a stable hover.
- Slowly lower the throttle to descend and land gently.
- Power off the drone after landing.
Flight Planning and Maneuvering
Careful flight planning is essential for safe and successful drone flights. This section covers factors to consider when planning a flight and various flight maneuvers.
Flight Planning Considerations
Before each flight, plan your route, considering weather conditions, airspace restrictions, and battery life. This helps ensure a safe and efficient flight.
- Check the weather forecast for wind speed, precipitation, and visibility.
- Verify airspace restrictions using a flight planning app or website.
- Calculate the flight time based on the drone’s battery life and planned maneuvers.
- Plan a safe return-to-home (RTH) route in case of unexpected issues.
Flight Maneuvers
This section describes basic and more complex drone maneuvers. Practice these maneuvers in a safe, open area before attempting them in more challenging environments.
- Basic Turns: Use the yaw control to rotate the drone smoothly.
- Ascents and Descents: Use the throttle to control altitude.
- Forward and Backward Movement: Use the pitch control to move the drone forward or backward.
- Sideways Movement: Use the roll control to move the drone left or right.
Beginner Flight Plan Table
This table illustrates a simple flight plan for beginners. Remember to always prioritize safety and stay within your skill level.
| Waypoint | Altitude (meters) | Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Takeoff Point | 1 | Ensure clear area | |
| Waypoint 1 | 5 | Move 10 meters forward | |
| Waypoint 2 | 5 | Move 10 meters to the right | |
| Waypoint 3 | 1 | Descend and land | Ensure safe landing area |
Drone Camera Operation and Photography/Videography
Capturing stunning photos and videos with your drone requires understanding your camera settings and composition techniques. This section will guide you through the process.
Drone Camera Settings
Familiarize yourself with your drone’s camera settings to achieve optimal results. Key settings include ISO, shutter speed, and aperture.
- ISO: Controls the sensitivity to light. Higher ISO values are useful in low-light conditions but can introduce noise.
- Shutter Speed: Controls how long the camera’s sensor is exposed to light. Faster shutter speeds freeze motion, while slower shutter speeds create motion blur.
- Aperture: Controls the size of the lens opening, affecting depth of field. A wider aperture (smaller f-number) creates a shallow depth of field, while a narrower aperture (larger f-number) creates a deeper depth of field.
Tips for High-Quality Photos and Videos
These tips will help you capture professional-looking drone footage.
- Shoot in the best possible lighting conditions. Avoid harsh midday sun.
- Use a tripod or other stabilizing device for smooth shots.
- Experiment with different camera angles and perspectives.
- Edit your footage to enhance its quality and create a compelling story.
Adjusting Camera Settings for Different Lighting

Adjust your camera settings based on the lighting conditions to optimize your shots.
- Bright Sunlight: Lower ISO, faster shutter speed.
- Overcast Conditions: Slightly higher ISO, moderate shutter speed.
- Low Light: Higher ISO, slower shutter speed (consider a tripod or image stabilization).
Composing Effective Drone Shots

Effective composition is key to creating visually appealing drone footage.
- Framing: Use the environment to frame your subject.
- Perspective: Use altitude and angles to create unique perspectives.
- Rule of Thirds: Position your subject off-center to create a more balanced and visually interesting composition.
- Leading Lines: Use natural lines in the landscape to guide the viewer’s eye.
Troubleshooting Common Drone Issues: How To Operate A Drone
Even experienced drone pilots encounter problems. This section provides troubleshooting steps for common issues.
Common Drone Problems
This section Artikels common problems and their potential solutions.
- Low Battery Warnings: Land immediately and recharge the battery.
- GPS Signal Loss: Move to an open area with a clear view of the sky and retry.
- Motor Malfunctions: Inspect the motors and propellers for damage. If necessary, contact support for repairs.
- Drone Failsafe: Most drones have a failsafe mechanism. This will typically cause the drone to automatically land safely.
Troubleshooting Guide Table
This table summarizes troubleshooting steps for common drone issues.
| Problem | Solution |
|---|---|
| Low Battery Warning | Land immediately and recharge the battery. |
| GPS Signal Loss | Move to an open area with a clear view of the sky and retry. |
| Motor Malfunction | Inspect motors and propellers for damage. Contact support if needed. |
| No Response from Controller | Check controller battery and connection to drone. Try re-pairing the devices. |
| Unexpected Drone Behavior | Check for interference. Ensure firmware is updated. |
Post-Flight Procedures and Maintenance
Proper post-flight procedures are crucial for maintaining your drone’s lifespan and ensuring its continued safe operation. This section details essential steps for storage and maintenance.
Post-Flight Procedures
After each flight, follow these steps to ensure your drone is properly stored and maintained.
- Power off the drone and remove the battery.
- Carefully inspect the drone for any damage or debris.
- Clean the drone’s body and propellers.
- Charge the battery according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Store the drone and its accessories in a safe, dry place.
Drone Maintenance
Regular maintenance extends the lifespan of your drone.
- Inspect propellers and motors for damage before each flight.
- Clean the drone’s sensors regularly.
- Check for firmware updates and install them as needed.
- Store the drone in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight.
Properly Stored Drone
A properly stored drone and its accessories present a neat and organized image. The drone itself sits securely in its designated case, possibly nestled in foam padding to prevent movement. The propellers are carefully stored, perhaps in a separate compartment or attached to the drone body but secured to prevent accidental damage. Batteries are stored separately, in a designated fire-resistant bag, and are kept away from other electronics.
The remote controller is also stored securely, perhaps in a dedicated pouch within the case. The entire case is clean and free of debris, giving an overall impression of well-maintained equipment ready for its next flight.
Mastering the art of drone operation involves a blend of technical skill and responsible practice. By diligently following pre-flight checklists, understanding drone controls, and planning your flights meticulously, you can unlock the potential of aerial photography and videography while ensuring the safety of yourself and others. Remember to always prioritize safety and adhere to all relevant regulations. With practice and careful attention to detail, you’ll be soaring through the skies with confidence, capturing breathtaking visuals from unique perspectives.
FAQ Summary
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource for this is available online; check out this comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone to gain a solid foundation. From there, practice and experience will further refine your skills in operating a drone safely and effectively.
Many user-friendly drones with GPS stabilization and beginner modes are ideal for starting. Look for models with features like automatic return-to-home and obstacle avoidance.
How long does a drone battery typically last?
Drone battery life varies significantly depending on the model and flight conditions. Expect flight times ranging from 15 to 30 minutes, sometimes longer. Always carry extra batteries.
What happens if I lose the drone’s GPS signal?
Most drones have a return-to-home function that will guide it back to its takeoff point. However, it’s crucial to maintain visual contact with the drone at all times.
Is drone insurance necessary?
Drone insurance is highly recommended, especially for commercial use or flights in populated areas. It protects you against liability in case of accidents or damage.
